
Beyond Meat does not carry fair-trade certifications for its coconut or canola oil sourcing. Despite this, coconut oil is considered by experts to be a more sustainable fat choice for the environment: “compared to a competing product like palm oil, coconut oil does not require heavy land use, i.e. However, the coconut oil must be produced and shipped by freight from Malaysia or Indonesia, a distance of over 20,000 miles to Beyond Food’s processing facilities in the United States. The rapeseed canola oil used is produced in Canada and the United States (Heller and Keoleian). A secondary protein used comes from brown rice and helps to form a complete protein profile.Īside from water and pea protein, the remainder of the product is almost entirely oil. Roquette, the company with which Beyond Meat contracts for plant protein, sells these byproducts to industries such as nutrition, pharmaceuticals, and pet foods (Roquette). At a production plant, the starch, fiber, and hull of peas are separated from the protein and sold in separate markets where their impact is harder to measure. Production of peas accounts for 20% of Beyond meat’s total greenhouse gas emissions (Heller and Keoleian). This protein is mainly processed from yellow peas harvested from Saskatchewan or Manitoba in Canada, and growing peas is the primary source of land use for the product at roughly 1 acre per ton annually (Arnason). The core of the Beyond meat product is its pea protein. As with many commercial food products, transportation and its associated emissions remains a major consideration when calculating the sustainability of Beyond meat. In 2020, Beyond Meat opened new production facilities in China and the Netherlands, allowing them to reduce emissions and energy when distributing at these locations but increasing transport distance for some ingredients, especially those primarily produced in North America (Beyond Meat, News Release). The transportation of materials to these facilities create emissions and consume energy based on the distance they must be moved. Their products aim to be vegan and do not feature animal ingredients or testing of any kind.īeyond Meat has several production facilities in the United States (Cosgrove). During production, corrugated cardboard cartons are also used (Heller and Keoleian).

The patties are sat onto wax coated paper and the final product is placed inside a paperboard sleeve. The product is packaged using two plastics: a polypropylene tray with a polyethylene sealant. Coloring is used in the form of beet juice extract. Producing the pea protein isolate requires peas and water, and the canola oil is pressed from rapeseed. Despite this, Heller and Keoleian’s report is peer-reviewed by independent sources and a window into where Beyond’s raw materials come from.īeyond meat is primarily made from water, pea protein isolate, rice protein, canola oil, and coconut oil, along with small quantities of other ingredients, vitamins, and minerals (Beyond Meat, Ingredients). More transparent and independent reporting is needed to verify whether these findings are accurate. Outside of this report, Beyond Meat has remained nearly completely opaque about its product lifecycle, earning it a 0% score on its weighted environmental disclosure ratio in an analysis by Trucost (Bitter and Tsao). Keoleian, exposes most of what we know about Beyond meat’s operations and supply chain, despite a potential for bias from its funding (Wolf). In 2018, Beyond Meat commissioned the University of Michigan to perform an analysis on the lifecycle of Beyond meat products. Our life cycle assessment of their flagship alternative beef product demonstrates that collecting and processing the raw materials used to create Beyond meat, mainly peas, takes significantly less energy, creates fewer emissions, and is generally more sustainable compared to farming traditional beef.

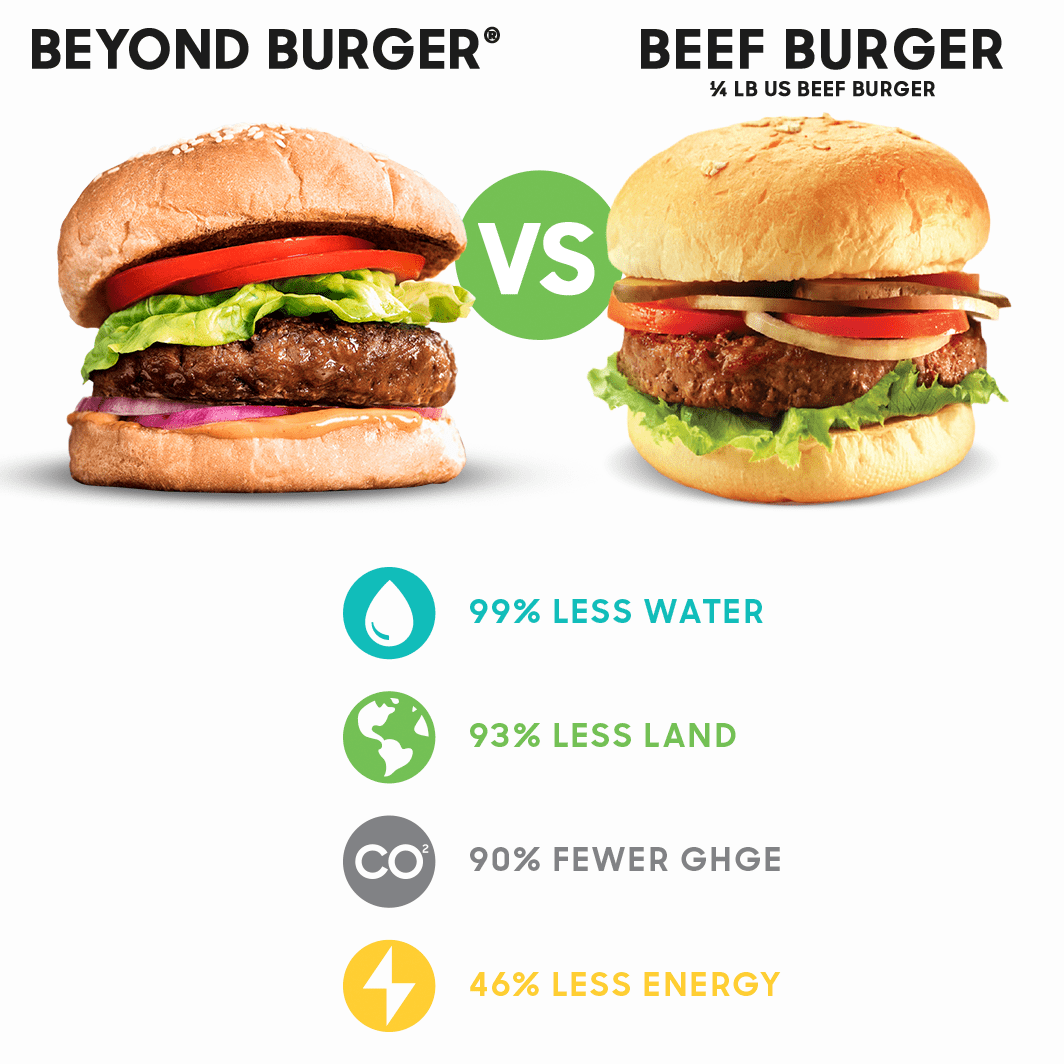
Ingredients for the plant food constitute the majority of emissions, energy, and water usage of the product’s lifecycle, followed by packaging materials and then production. Beyond Meat, the company that manufactures Beyond meat and other similar products, makes the claim that it is an eco-conscious alternative to eating real meat, a claim that we will examine through an analysis of their consumption and usage of raw materials.

Beyond meat is a form of “plant-based meat”-an imitation meat that attempts to resemble the experience and nutritional profile of beef without the use of animals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
